A new anti-cancer strategy: Overriding tumor edits
Cancers are clever and often find ways to dodge people’s immune systems, making them hard to eradicate. Immunotherapies such as CAR-T cells and checkpoint inhibitors can sharpen the immune system’s attack and cure the cancer. But they don’t work for most solid tumors. We now know that tumors can edit their genes to evade immune ... Read More about A new anti-cancer strategy: Overriding tumor edits
Humble cells in a little-known organ manage brain inflammation
Deep in the brain, sheets of tissue known as the choroid plexus produce cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and act as a protective barrier between the brain and CSF. But the lab of Maria Lehtinen, PhD, at Boston Children’s Hospital has shown that the little-known choroid plexus does much more. For example, it secretes factors that promote ... Read More about Humble cells in a little-known organ manage brain inflammation
Creating the next generation of mRNA vaccines
During the COVID-19 pandemic, mRNA vaccines came to the rescue, developed in record time and saving lives worldwide. Researchers in the Precision Vaccines Program at Boston Children’s Hospital have developed two novel technologies that could make these and future mRNA vaccines more potent and longer-lasting — at smaller doses and with fewer side effects. The ... Read More about Creating the next generation of mRNA vaccines
Tracking influenza in its first battleground: The nose
The answer to curbing influenza could be right under our noses — or, more accurately, inside them. New research maps happenings in the nose during the course of influenza in exquisite detail, and could potentially lead to new targets and more effective nasal flu vaccines. The nose is often the gateway to respiratory infections, where ... Read More about Tracking influenza in its first battleground: The nose
From ‘hit to vial’: Discovery and optimization of a promising vaccine adjuvant
Many vaccines are only partially effective, have waning efficacy, or do not work well in the very young or the very old. For more than a decade, Ofer Levy, MD, PhD, and David Dowling, PhD, in the Precision Vaccines Program at Boston Children’s Hospital, have tried improving vaccines by adding compounds known as adjuvants to ... Read More about From ‘hit to vial’: Discovery and optimization of a promising vaccine adjuvant
Boosting vaccines for the elderly with ‘hyperactivators’
As we age our immune systems start to flag, leaving us more susceptible to cancer and infections — and less responsive to vaccines and cancer immunotherapies. Going to the heart of the problem, Jonathan Kagan, PhD, a researcher in immunology at Boston Children’s Hospital, has identified a way to rejuvenate the elderly immune system. His ... Read More about Boosting vaccines for the elderly with ‘hyperactivators’
A deeper understanding of inflammatory pain could reveal new solutions
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as ibuprofen are the main go-to for inflammatory pain caused by wounds, infection, sunburn, arthritis, and other triggers. NSAIDs work pretty well, but chronic use can cause side effects, and they aren’t equally effective for all sources of pain. Could we identify a more effective, safer analgesic that doesn’t involve ... Read More about A deeper understanding of inflammatory pain could reveal new solutions
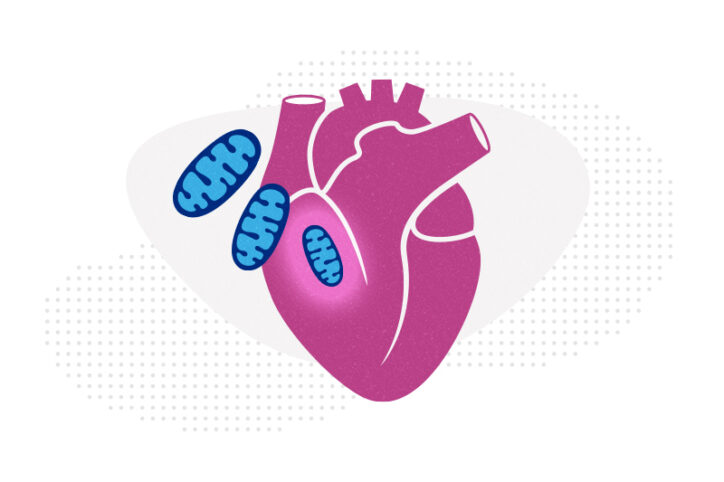
Mitochondrial transfer restores heart muscle — but how?
Transferring mitochondria from a patient’s healthy skeletal muscle to damaged, ischemic heart tissue has been shown to restore heart muscle, increase energy production, and improve ventricular function. After pioneering preclinical work by James McCully, PhD, at Boston Children’s Hospital about a decade ago, cardiac surgeons led by Sitaram Emani, MD, have been testing it as ... Read More about Mitochondrial transfer restores heart muscle — but how?
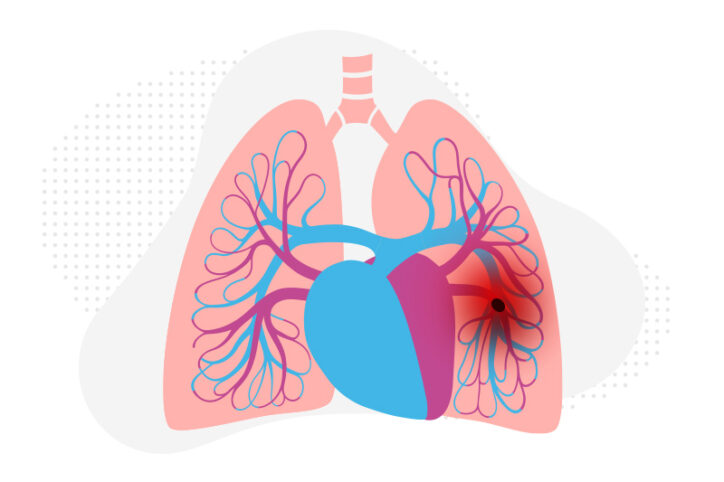
Study suggests hypoxia overexpression causes pericytes to contribute to pulmonary hypertension
Pericytes, the multifunctional cells that work within the walls of capillaries, have been a subject of focus in the study of vascular development, cerebral blood flow, cancer, and neurodevelopment diseases. But pericytes hadn’t been truly studied for their potential role in pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) until they landed under the microscopes of Boston Children’s researchers. They recently ... Read More about Study suggests hypoxia overexpression causes pericytes to contribute to pulmonary hypertension
Mending injured hearts: Lessons from newborns?
When the heart is injured, as in a myocardial infarction, the damaged heart muscle cannot regenerate — instead, scar tissue forms. Cardiomyocytes, the heart muscle cells that generate contractile force, are lost for good. Yet, in mouse models, the hearts of newborns regenerate readily after injury. How are newborn hearts able to recover? What are ... Read More about Mending injured hearts: Lessons from newborns?