Blood across our lifetimes: An age-specific ‘atlas’ tells a dynamic story
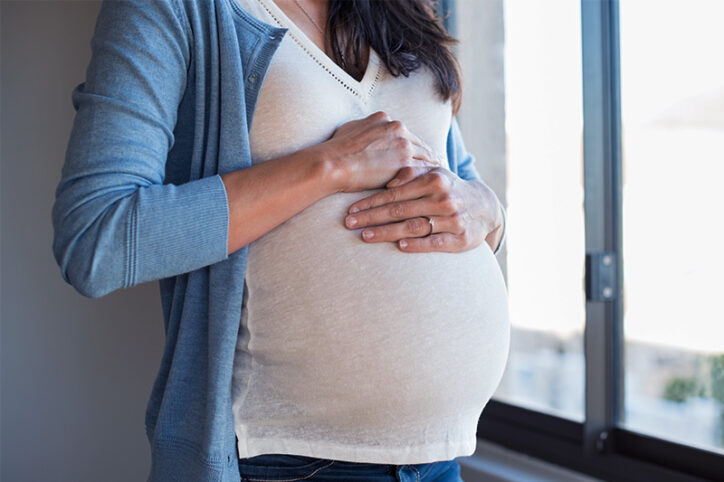
The stem cells that form our blood, also known as hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs), are with us throughout our lives. A new study reveals how HSCs ramp up and pivot their activities depending on the body’s needs at the time, from before we’re born until old age. Researchers at Dana-Farber/Boston Children’s Cancer and Blood Disorders ... Read More about Blood across our lifetimes: An age-specific ‘atlas’ tells a dynamic story
Could a pill treat sickle cell disease?
The new gene therapies for sickle cell disease — including the gene-editing treatment Casgevy, based on research at Boston Children’s Hospital — have been game-changing for the patients who have received them. But Stuart Orkin, MD, the Boston Children’s hematologist whose work led the way to Casgevy, wants to go even further. “The editing therapy ... Read More about Could a pill treat sickle cell disease?
Injected microbubbles could be a safe way to deliver emergency oxygen
For years, researchers and clinicians have been trying to find a way to rapidly deliver oxygen to patients when traditional means of oxygenation are difficult or ineffective during critical moments of cardiac or respiratory arrest. Sometimes, hypoxemia caused by airway obstruction or lung disease can be so severe that methods to boost low-oxygen levels (including ... Read More about Injected microbubbles could be a safe way to deliver emergency oxygen
A universal gene therapy for Diamond-Blackfan anemia is poised for clinical testing
Diamond-Blackfan anemia (DBA), first described at Boston Children’s Hospital in 1938, is a rare blood disorder in which the bone marrow cannot make mature, functioning red blood cells. Children with this life-threatening anemia have few treatment options. A small handful with a well-matched donor can be cured with bone marrow transplant, but most rely on ... Read More about A universal gene therapy for Diamond-Blackfan anemia is poised for clinical testing
Skin organoid could guide new treatments for skin conditions, hair loss
What does it take to build healthy skin? Two research groups converged on this question from different angles. They’ve now produced the most detailed view to date of the cell types and cell collaborations that go into creating our body’s largest organ. Several years ago, Karl Koehler, PhD, and colleagues at Boston Children’s Hospital used ... Read More about Skin organoid could guide new treatments for skin conditions, hair loss
Mutations during prenatal development may contribute to schizophrenia
Schizophrenia is known to have a genetic component, and variants in 10 genes have been identified as markedly increasing schizophrenia risk. But together, these genes account for under 5 percent of cases. Now, a pilot study in the journal Science suggests another important contributor to schizophrenia: distinctive patterns of non-inherited (somatic) mutations. These mutations appear ... Read More about Mutations during prenatal development may contribute to schizophrenia
Delving into the causes of attention deficits: Childhood adversity, lost sleep, and dopamine
New research on the effects of adversity in childhood ties together stress, sleep loss, and attention deficits later in life. It also uncovers some of the underlying brain biology and potential treatment approaches — while revealing a puzzling sex-specific effect. The lab of Takao Hensch, PhD, has long studied time windows during development — commonly ... Read More about Delving into the causes of attention deficits: Childhood adversity, lost sleep, and dopamine
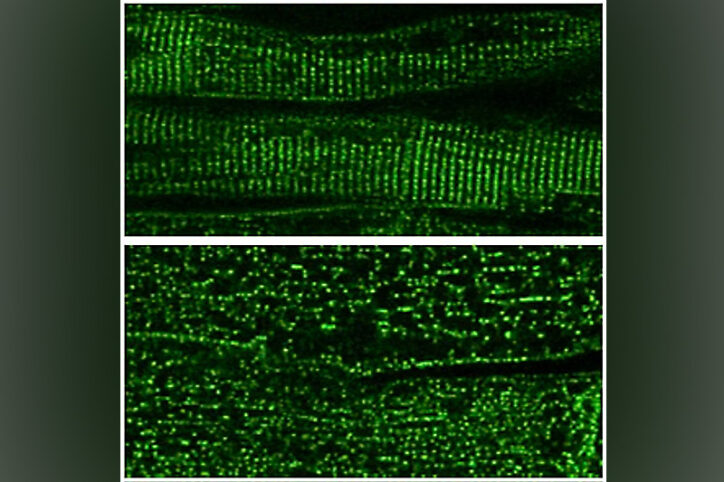
Shoring up heart muscle’s mini ‘managers’ to treat heart failure
Our heart muscle is studded with tiny dyads, intricately designed structures that manage incoming electrical signals and calcium release to coordinate our heartbeats. Could gene therapy help maintain dyads’ structure and boost the function of failing hearts? A new study suggests it can. “We know that in heart failure from many causes, dyads become disorganized,” says ... Read More about Shoring up heart muscle’s mini ‘managers’ to treat heart failure
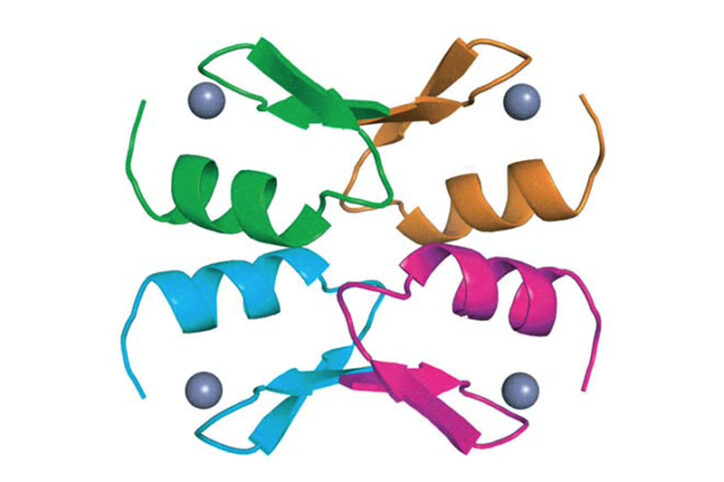
Finding a possible genetic treatment for rare arrhythmias
Variants in a gene that plays a key role in heart function can cause potentially life-threatening arrhythmia syndromes known as calmodulinopathy. Calmodulinopathy is rare and causes arrhythmias that are poorly treated by current options. Boston Children’s cardiologist William Pu, MD, believes he has found a promising custom genetic treatment: antisense oligonucleotides that deplete the disease-causing gene product. ... Read More about Finding a possible genetic treatment for rare arrhythmias
Curbing blood cancers by teaching immune cells to kill mutant stem cells
Blood stem cells, which give rise to all of our blood cell types, undergo a quality assurance process after they’re born. As the lab of Leonard Zon, MD, director of the Stem Cell Research program at Boston Children’s, has documented, immune cells known as macrophages interact with each newly born cell. They engulf and eat ... Read More about Curbing blood cancers by teaching immune cells to kill mutant stem cells