Archive for cellular and molecular medicine
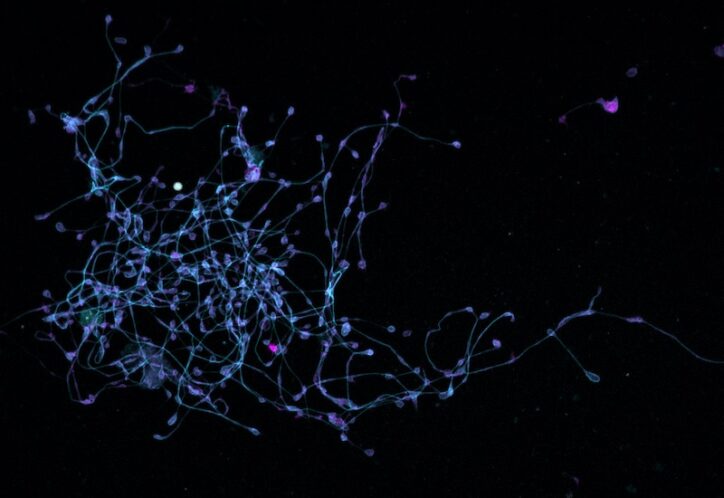
A new druggable cancer target: RNA-binding proteins on the cell surface
In 2021, research led by Ryan Flynn, MD, PhD, and his mentor, Nobel laureate Carolyn Bertozzi, PhD, opened a new chapter in biology, characterizing a new kind of player on the cell surface: glycoRNAs. Extending this discovery recently in Cell, Flynn and colleagues showed that glycoRNAs form highly organized clusters with RNA-binding proteins on the ... Read More about A new druggable cancer target: RNA-binding proteins on the cell surface
Bringing order to disorder: Jhullian Alston, PhD
Proteins typically fold into orderly, predictable three-dimensional structures that dictate how they will interact with other molecules. Jhulian Alston, PhD, is drawn to intrinsically disordered proteins, whose key feature is a lack of structure. They are difficult to study and far less explored. “They’re floppy, they don’t have specific folds, they can’t slot into each ... Read More about Bringing order to disorder: Jhullian Alston, PhD
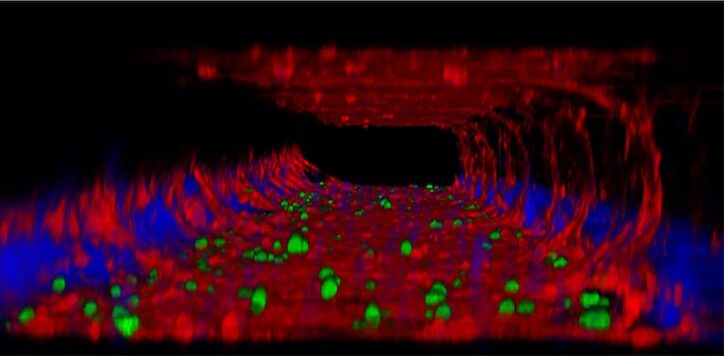
Tracking influenza in its first battleground: The nose
The answer to curbing influenza could be right under our noses — or, more accurately, inside them. New research maps happenings in the nose during the course of influenza in exquisite detail, and could potentially lead to new targets and more effective nasal flu vaccines. The nose is often the gateway to respiratory infections, where ... Read More about Tracking influenza in its first battleground: The nose
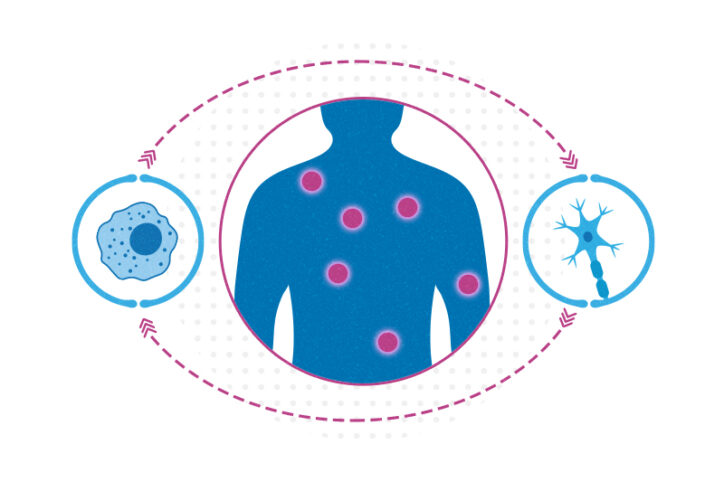
A deeper understanding of inflammatory pain could reveal new solutions
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as ibuprofen are the main go-to for inflammatory pain caused by wounds, infection, sunburn, arthritis, and other triggers. NSAIDs work pretty well, but chronic use can cause side effects, and they aren’t equally effective for all sources of pain. Could we identify a more effective, safer analgesic that doesn’t involve ... Read More about A deeper understanding of inflammatory pain could reveal new solutions
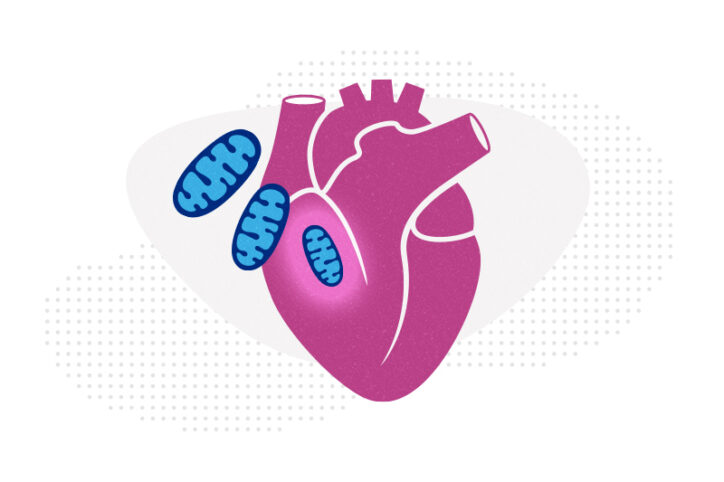
Mitochondrial transfer restores heart muscle — but how?
Transferring mitochondria from a patient’s healthy skeletal muscle to damaged, ischemic heart tissue has been shown to restore heart muscle, increase energy production, and improve ventricular function. After pioneering preclinical work by James McCully, PhD, at Boston Children’s Hospital about a decade ago, cardiac surgeons led by Sitaram Emani, MD, have been testing it as ... Read More about Mitochondrial transfer restores heart muscle — but how?
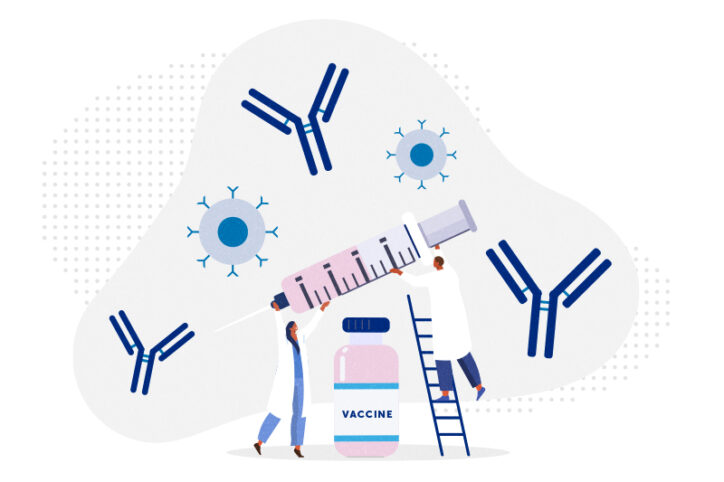
Building better antibodies, curbing autoimmunity: New insights on B cells
When we’re vaccinated or exposed to an infection, our B cells spring into action, churning out antibodies that are increasingly potent, specific, and protective. This happens through an iterative process known as affinity maturation. Two labs at Boston Children’s Hospital have come up with different ways to enhance affinity maturation and help B cells make ... Read More about Building better antibodies, curbing autoimmunity: New insights on B cells
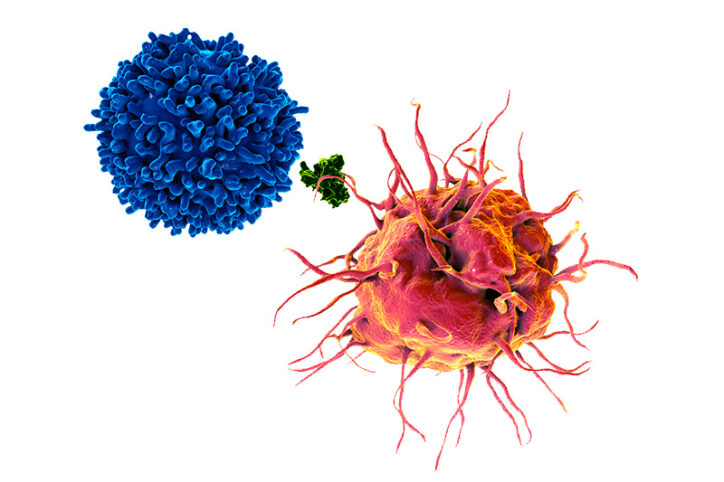
Exposing a tumor’s antigens to enhance immunotherapy
Successful immunotherapy for cancer involves activating a person’s own T cells to attack the tumor. But some tumors have a trick: They hide themselves from the immune system by preventing their antigens from being displayed, a necessary step in activating T cells. In new work published in Science, researchers in the Program in Cellular and ... Read More about Exposing a tumor’s antigens to enhance immunotherapy
Could the right dietary fat help boost platelet counts?
Aside from transfusions, there currently is no way to boost people’s platelet counts, leaving them at risk for uncontrolled bleeding. Could something as simple as a dietary change raise platelet counts in people with low levels, such as cancer patients receiving chemotherapy? New science out of the lab suggests that the answer might be yes. ... Read More about Could the right dietary fat help boost platelet counts?
Tackling an aggressive, treatment-resistant lymphoma where it lives
Anaplastic large cell lymphoma, a form of non-Hodgkin lymphoma, is the most common aggressive lymphoma in children. Chemotherapy and radiation fail to cure about 30 percent of cases. When tumors are driven by the oncogene ALK — which is the case for the majority of children — kinase inhibitor drugs like crizotinib are very effective ... Read More about Tackling an aggressive, treatment-resistant lymphoma where it lives
Tagged: cancer, cellular and molecular medicine, lymphoma
One-time treatment could block a deadly form of graft-versus-host disease
Even when a bone marrow transplant cures leukemia or lymphoma, patients can still pass away from graft-versus-host disease (GVHD), in which T cells in the donor graft attack the recipient’s own tissues. Leslie Kean, MD, PhD, director of stem cell transplant at Dana-Farber/Boston Children’s Cancer and Blood Disorders Center, has long sought to prevent this ... Read More about One-time treatment could block a deadly form of graft-versus-host disease