Archive for cellular and molecular medicine
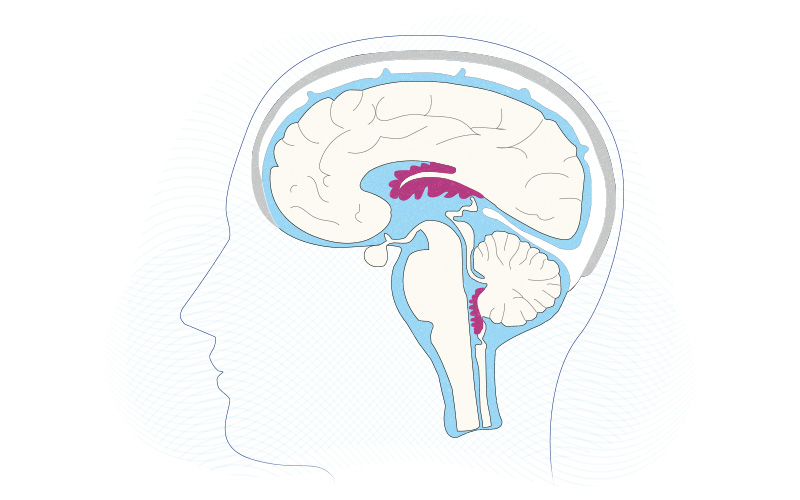
An ‘atlas’ of the choroid plexus across the lifespan
Once viewed merely as a producer of the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) bathing the brain and spinal cord, the choroid plexus is now known to be a key player in brain development and immunity. These fronds of brain tissue, located in the CSF-filled brain cavities known as ventricles, secrete instructive cues into the CSF to regulate ... Read More about An ‘atlas’ of the choroid plexus across the lifespan
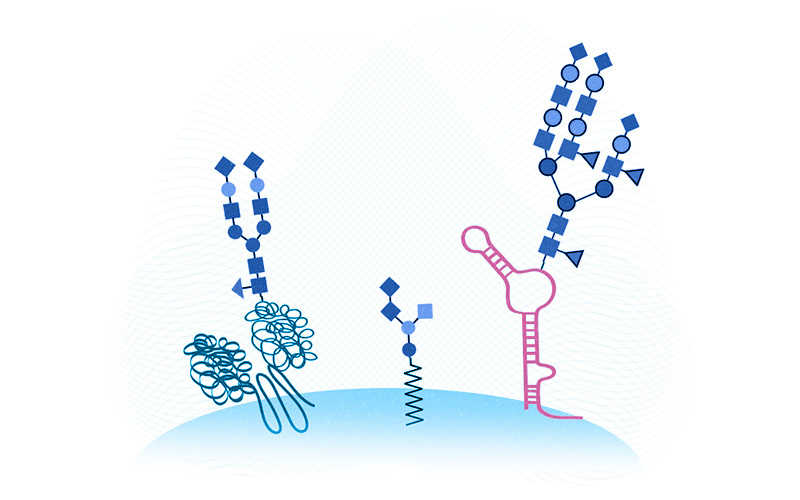
When worlds collide: Glycosylated RNAs upend cell biology as we know it
Cells in our body bristle with sugars known as glycans that other cells can recognize via specialized receptors. Glycans attach to and modify proteins and fats, thereby influencing how proteins fold, how cues are trafficked between cells, and other cell-to-cell interactions. As just one example of glycans’ importance, our blood types (A, B, O) depend ... Read More about When worlds collide: Glycosylated RNAs upend cell biology as we know it
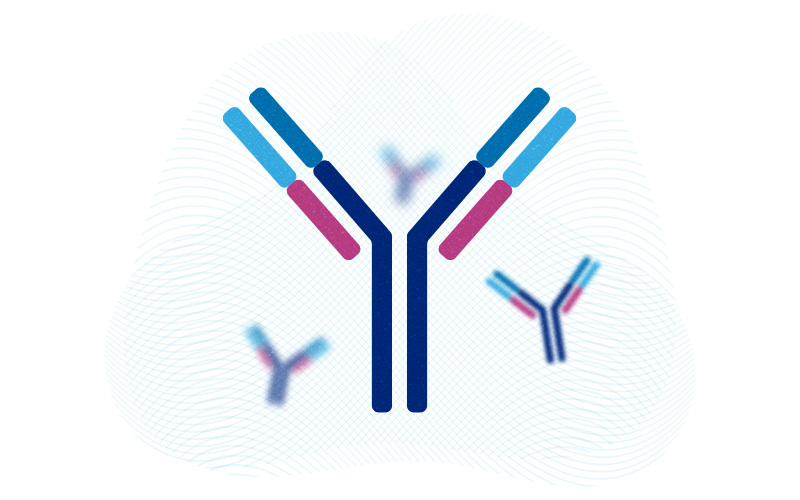
Diversifying therapeutic antibodies: From one, come many with potential different uses
A new method for producing antibodies against disease could result in a wider variety of drugs for infectious diseases, immune disease, and even cancer. The immune system naturally produces enormous varieties of antibodies to fight diseases. Therapeutic antibodies — antibodies created against specific therapeutic targets — have been used for decades to either rev up ... Read More about Diversifying therapeutic antibodies: From one, come many with potential different uses
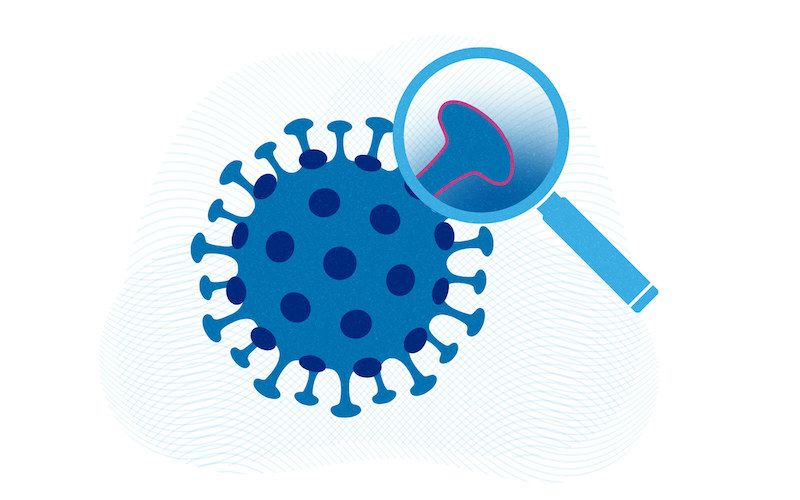
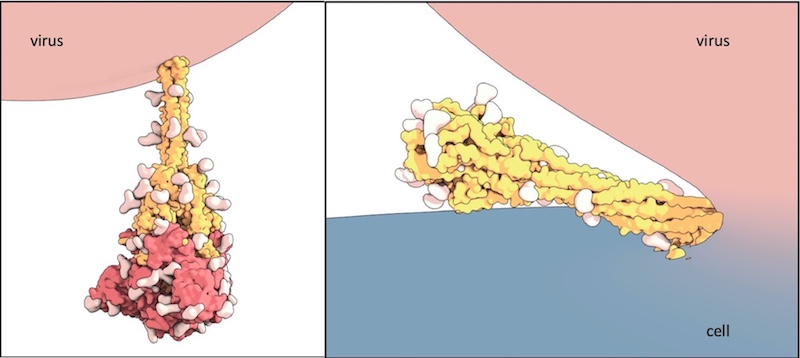
Sturdier spikes may explain SARS-CoV-2 variants’ faster spread
The fast-spreading U.K., South Africa, and Brazil variants are raising concerns and questions about whether current COVID-19 vaccines will protect against them. A structural biology study led by Bing Chen, PhD, at Boston Children’s Hospital now reveals how the D614G mutation — carried by all three variants — makes SARS-CoV-2 spread faster. Key takeaways: The main ... Read More about Sturdier spikes may explain SARS-CoV-2 variants’ faster spread
Specialized T cells protect against the deadliest form of malaria
Each year, there are about 230 million cases of malaria globally. Children under the age of 5 are at highest risk of serious illness and death, accounting for about 265,000 deaths, or nearly 70 percent of all malaria deaths worldwide. Despite significant time and money poured into efforts to develop an effective malaria vaccine, the ... Read More about Specialized T cells protect against the deadliest form of malaria
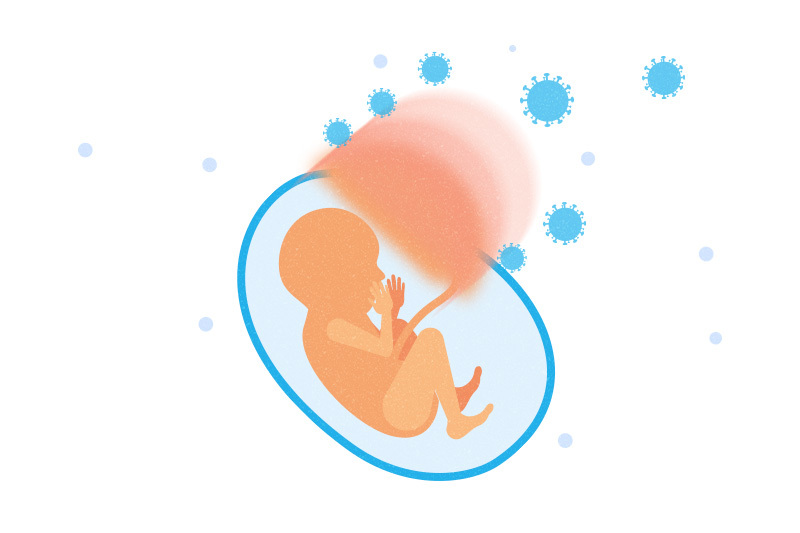
How does the placenta protect unborn babies from COVID-19?
Evidence has shown that pregnancy is a risk factor for severe illness in women with COVID-19. A recent CDC study reviewed case reports of approximately 400,000 women aged 15 to 44 with symptomatic COVID-19. Those who were pregnant had a roughly tripled likelihood of ICU admission and invasive ventilation and 70 percent higher mortality. Yet ... Read More about How does the placenta protect unborn babies from COVID-19?
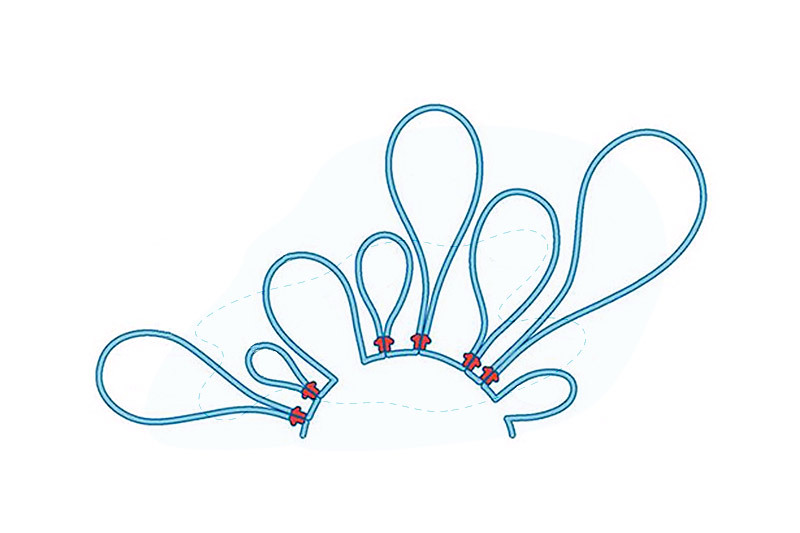
Chromatin regulation enables generation of diverse antibodies
We need a variety of antibody types to help fight off invading foreign pathogens and our genome is exquisitely tuned to produce them to meet emerging needs. A new study finds that not just our DNA, but its configuration and packaging, help us generate diverse antibodies. Key takeaways Chromatin loop extrusion leads to creation of ... Read More about Chromatin regulation enables generation of diverse antibodies
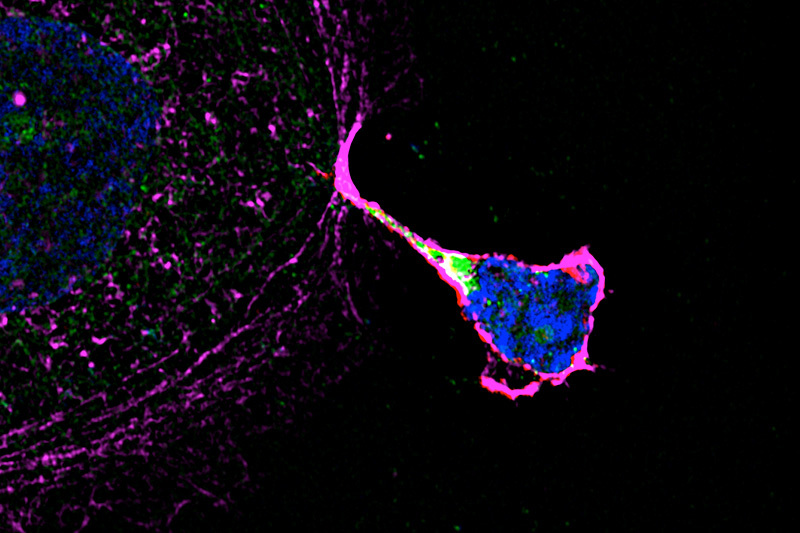
Natural killer cells: Protect the placenta cell but kill the infection
Infections that reach the placenta can lead to spontaneous abortions, intrauterine growth restriction, congenital abnormalities, and premature births. New research from the laboratory of Judy Lieberman, MD, PhD, and colleagues at Harvard University shows that a group of cells near the site where the placenta attaches to the uterine wall plays an essential role in ... Read More about Natural killer cells: Protect the placenta cell but kill the infection
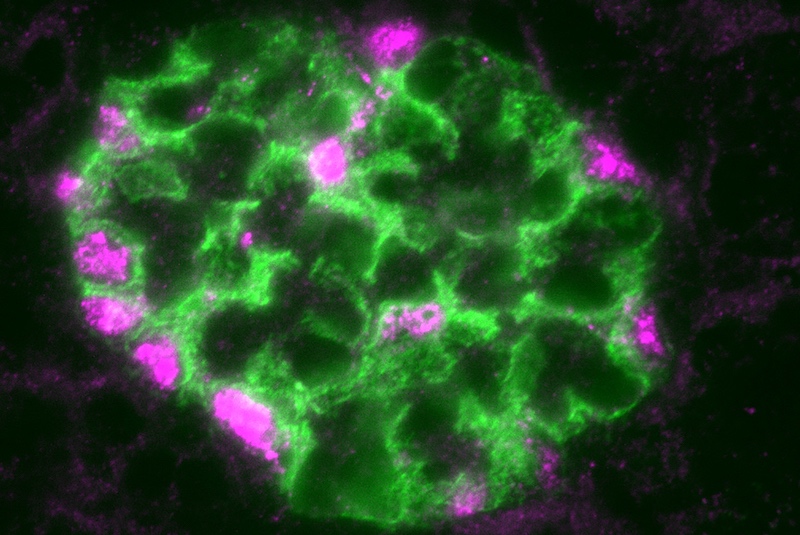
A master regulator of kidney health?
End-stage kidney disease often begins with injury to podocytes. These highly specialized cells are a critical part of the glomeruli, clusters of capillaries that serve as the filtration units in our kidneys’ tightly-packed nephrons. As their name suggests, podocytes extend tiny foot processes to intermingle with the capillaries and filter the blood, maintaining the proper ... Read More about A master regulator of kidney health?
Capturing SARS-CoV-2’s shape-shifting spike protein
The rod-like spike proteins on the surface of SARS CoV-2 are the tip of the spear of the COVID-19 pandemic. The spikes bind to human cells via the ACE2 receptor and then dramatically change shape. They jack-knife, folding in on themselves to fuse their own membrane with the membrane of our cells. And that opens ... Read More about Capturing SARS-CoV-2’s shape-shifting spike protein