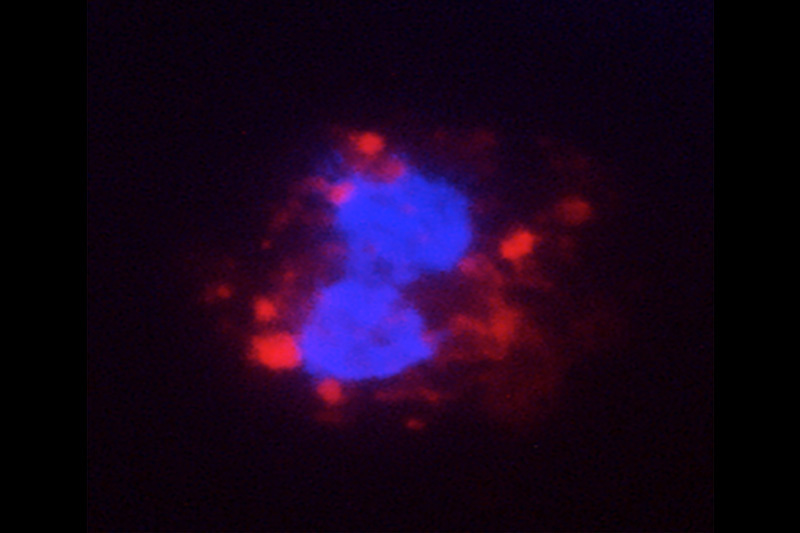
Diversifying therapeutic antibodies: From one, come many with potential different uses
A new method for producing antibodies against disease could result in a wider variety of drugs for infectious diseases, immune disease, and even cancer. The immune system naturally produces enormous varieties of antibodies to fight diseases. Therapeutic antibodies — antibodies created against specific therapeutic targets — have been used for decades to either rev up ... Read More about Diversifying therapeutic antibodies: From one, come many with potential different uses
Sturdier spikes may explain SARS-CoV-2 variants’ faster spread
The fast-spreading U.K., South Africa, and Brazil variants are raising concerns and questions about whether current COVID-19 vaccines will protect against them. A structural biology study led by Bing Chen, PhD, at Boston Children’s Hospital now reveals how the D614G mutation — carried by all three variants — makes SARS-CoV-2 spread faster. Key takeaways: The main ... Read More about Sturdier spikes may explain SARS-CoV-2 variants’ faster spread
Looking for cancer’s Achilles heel: The Pediatric Cancer Dependency Map
Thanks to developments in precision medicine, some adult cancers are now treated with designer drugs that target the genetic mutations that caused them. But most children with cancer have not reaped the same benefits. Unlike adult cancers, childhood cancers carry few genetic mutations. And the mutations these tumors do have are typically harder to make ... Read More about Looking for cancer’s Achilles heel: The Pediatric Cancer Dependency Map
How do patients with cystic fibrosis respond to COVID-19? An ‘airway in a dish’ may give answers
So far, based on clinical data, patients with cystic fibrosis (CF) don’t appear to be especially susceptible to COVID-19. And when they do get infected, they don’t seem to get sicker. But Ruobing (Ruby) Wang, MD, who cares for patients with CF in the Division of Pulmonary Medicine at Boston Children’s Hospital, thinks there is ... Read More about How do patients with cystic fibrosis respond to COVID-19? An ‘airway in a dish’ may give answers
Specialized T cells protect against the deadliest form of malaria
Each year, there are about 230 million cases of malaria globally. Children under the age of 5 are at highest risk of serious illness and death, accounting for about 265,000 deaths, or nearly 70 percent of all malaria deaths worldwide. Despite significant time and money poured into efforts to develop an effective malaria vaccine, the ... Read More about Specialized T cells protect against the deadliest form of malaria
‘Mosaic’ gene mutations could explain some cases of autism
The causes of autism remain mysterious. Scientists have linked autism spectrum disorder to a long list of genes, but most children with autism have no known explanation. Two new studies add to the picture, implicating mutations that affect only a fraction of a child’s cells. Called mosaic mutations, they open a new avenue for research ... Read More about ‘Mosaic’ gene mutations could explain some cases of autism
Therapy developed at Boston Children’s stops preeclampsia before it starts
Preeclampsia occurs in about 3 to 5 percent of all pregnancies. Characterized by very high maternal blood pressure, it can lead to serious, sometimes fatal, complications in both mother and baby. In severe cases, early delivery is often the only effective treatment, usually before the baby’s lungs are fully developed. Researchers within the Division of ... Read More about Therapy developed at Boston Children’s stops preeclampsia before it starts
Botulism breakthrough? Taming botulinum toxin to deliver therapeutics
While rare, botulism can cause paralysis and is potentially fatal. It is caused by nerve-damaging toxins produced by Clostridium botulinum — the most potent toxins known. These toxins often lurk in contaminated food (home canning being a major culprit). Infants can also develop botulism from ingesting C. botulinum spores in honey, soil, or dust; the ... Read More about Botulism breakthrough? Taming botulinum toxin to deliver therapeutics
Tough yet flexible: Biologically inspired adhesive may improve fetal surgery
In children with spina bifida, the neural tube that forms the spinal cord and brain doesn’t close during early prenatal development. That leaves the nerves of the spinal cord exposed to potential damage from fetal movement and the surrounding amniotic fluid. While surgeons can repair spina bifida soon after birth, the ideal would be to ... Read More about Tough yet flexible: Biologically inspired adhesive may improve fetal surgery
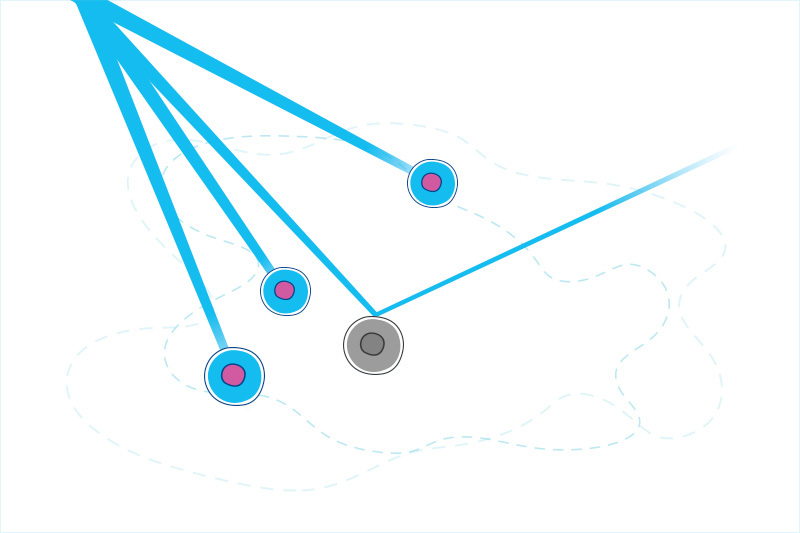
Missed signals? A new way we vary from each other biologically
Genetics has made huge strides over the past 20 years, from the sequencing of the human genome to a growing understanding of factors that turn genes on and off, namely transcription factors and the DNA “enhancer” sequences they bind to. New research from Boston Children’s Hospital introduces another previously unknown layer of human genetics. It ... Read More about Missed signals? A new way we vary from each other biologically