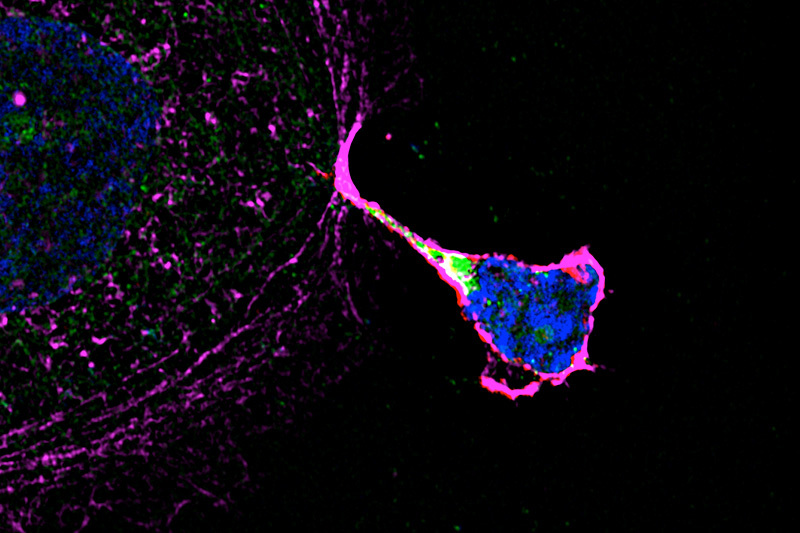
Natural killer cells: Protect the placenta cell but kill the infection
Infections that reach the placenta can lead to spontaneous abortions, intrauterine growth restriction, congenital abnormalities, and premature births. New research from the laboratory of Judy Lieberman, MD, PhD, and colleagues at Harvard University shows that a group of cells near the site where the placenta attaches to the uterine wall plays an essential role in ... Read More about Natural killer cells: Protect the placenta cell but kill the infection
Gene therapy’s future may be all about the bases
Gene therapy offers the possibility of a cure for many genetic disorders, especially those involving a single gene. The first kind of gene therapy used a virus to carry a corrected copy of the gene into people’s cells. When the early viral vectors used in the 1990s were found to have off-target effects, sometimes even ... Read More about Gene therapy’s future may be all about the bases
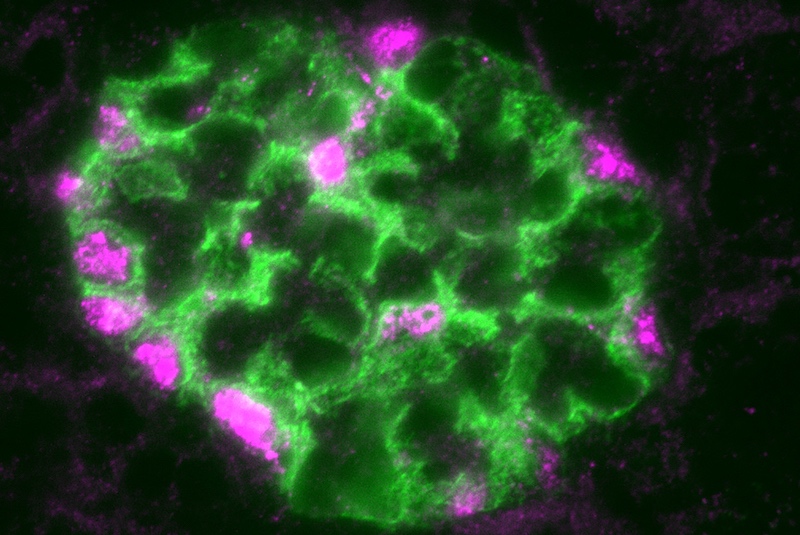
A master regulator of kidney health?
End-stage kidney disease often begins with injury to podocytes. These highly specialized cells are a critical part of the glomeruli, clusters of capillaries that serve as the filtration units in our kidneys’ tightly-packed nephrons. As their name suggests, podocytes extend tiny foot processes to intermingle with the capillaries and filter the blood, maintaining the proper ... Read More about A master regulator of kidney health?
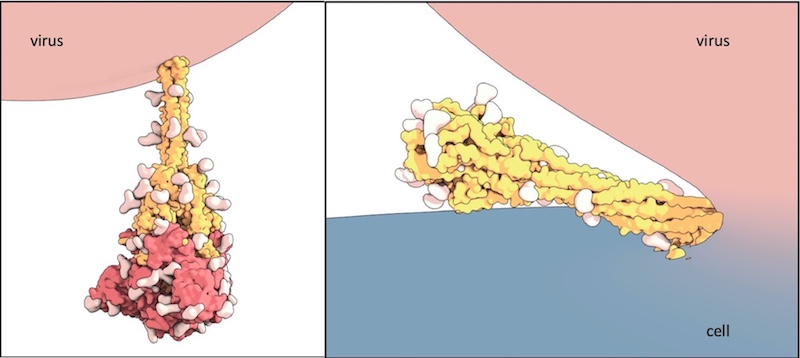
Capturing SARS-CoV-2’s shape-shifting spike protein
The rod-like spike proteins on the surface of SARS CoV-2 are the tip of the spear of the COVID-19 pandemic. The spikes bind to human cells via the ACE2 receptor and then dramatically change shape. They jack-knife, folding in on themselves to fuse their own membrane with the membrane of our cells. And that opens ... Read More about Capturing SARS-CoV-2’s shape-shifting spike protein
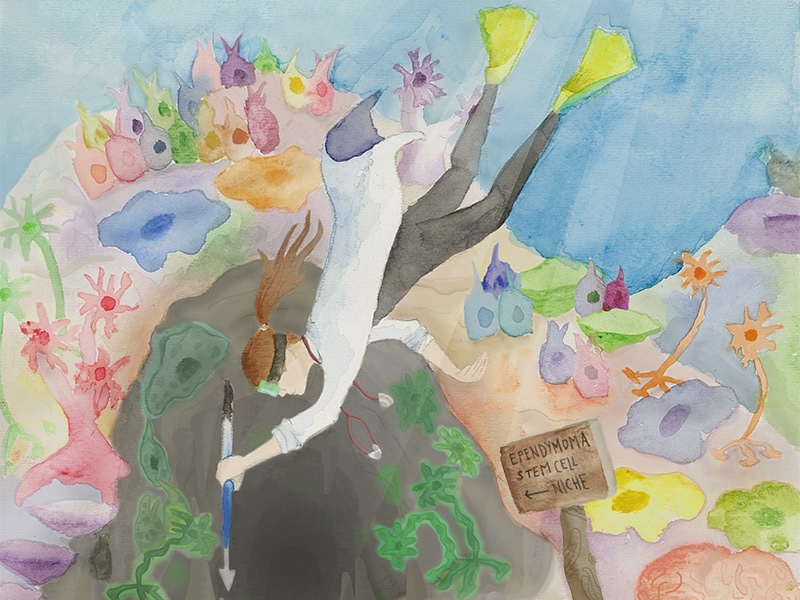
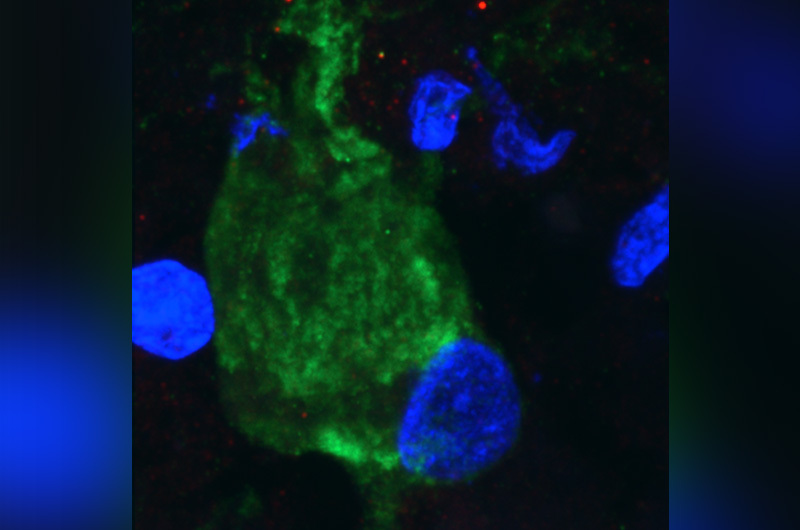
Diving into the dark side of ependymoma
Mariella Filbin, MD, PhD, a neuro-oncologist at Dana-Farber/Boston Children’s Cancer and Blood Disorders Center, is driven by a desire to find new therapies for some of the hardest-to-treat pediatric brain tumors. At the core of her work is an effort to uncover the events that shape tumor development. Key takeaways:· Aggressive ependymoma tumors are stuck ... Read More about Diving into the dark side of ependymoma
New drug pathway linked with tuberous sclerosis
Tuberous sclerosis complex (TSC) is a neurological disorder causing non-cancerous tumors, called cortical tubers, to grow throughout the brain and body, as well as other conditions like epilepsy and autism. While medications are used to treat some of the manifestations of the disease, safe and more effective treatments targeting disease at a fundamental level are ... Read More about New drug pathway linked with tuberous sclerosis
Type III interferon in COVID-19: Protective or harmful?
Our immune system makes interferons and other cytokines to help us fight viruses. But in COVID-19, we’ve learned that they can also contribute to damaging, potentially life-threatening lung inflammation. New work published yesterday in the journal Science helps tease out the good from the bad for one interferon of interest: type III. Key takeaways. At ... Read More about Type III interferon in COVID-19: Protective or harmful?
Creating hairy human skin: Not as easy as you think
Key takeaways· Scientists have created the first cultured human skin capable of growing hair embedded with fat and nerve cells. · Potential applications include burn treatments, and testing medications and cosmetics· The skin organoid system developed is a proof of concept for creating other human organoids, such as the inner ear. For more than 40 ... Read More about Creating hairy human skin: Not as easy as you think
Gene therapy with a new base editing technique restores hearing in mice
Using a new genetic engineering technique, known as base editing, researchers from Boston Children’s Hospital and the Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard, have restored hearing in mice with a known recessive genetic mutation. Key takeaways· This is the first example of repairing a recessive gene mutation.· Repairing a single mutation in the Tmc1 gene restored partial hearing in ... Read More about Gene therapy with a new base editing technique restores hearing in mice
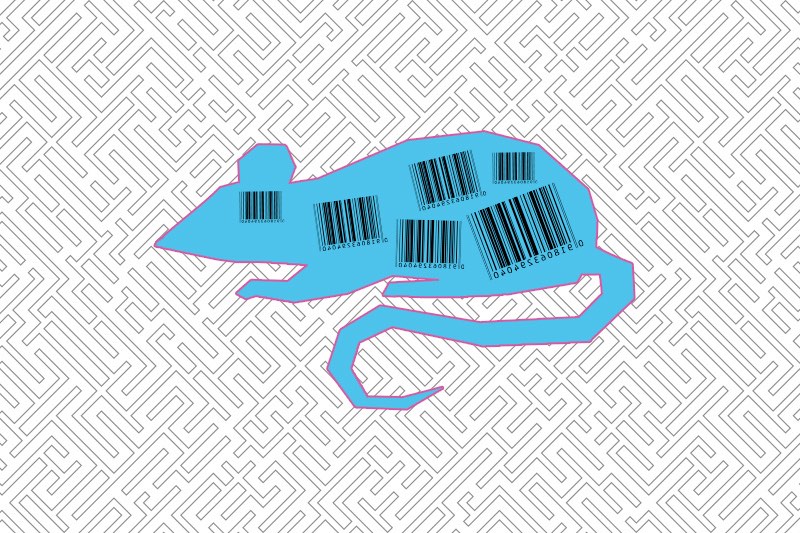
Tracking an organism’s development, cell by cell
A new mouse model allows scientists to track every cell in the body — from the embryo stage until adulthood. The system is the first of its kind and should yield a greater understanding of development, aging, and disease. Scientists described it last week in the journal Cell. “The dream of many developmental biologists for ... Read More about Tracking an organism’s development, cell by cell