Why do some people get severe COVID-19? The nose may know
The body’s first encounter with SARS-CoV-2, the virus behind COVID-19, happens in the nose and throat, or nasopharynx. A new study in the journal Cell suggests that the first responses in this battleground help determine who will develop severe disease and who will get through with mild or no illness. Building on work published last ... Read More about Why do some people get severe COVID-19? The nose may know
The surprisingly specific genetics of joint disease
A new study provides unexpected insights into the biology of two common, heritable orthopedic conditions: developmental dysplasia of the hip (DDH) and knee osteoarthritis (OA). The findings, published July 6 in Nature Communications, show how a gene can have different effects in different parts of the body. They also raise the possibility of preventive measures ... Read More about The surprisingly specific genetics of joint disease
A ‘pump’ gene’s surprising role in early brain formation
In polymicrogyria, the cortex of the brain has many irregular, small folds (gyria) and disorganization of its layers. Many affected children have severe developmental delay, intellectual disabilities, and epilepsy, and many need to use a wheelchair. Mutations in several different genes can cause this “overfolding of the brain” condition. Key takeaways The gene ATP1A3, associated ... Read More about A ‘pump’ gene’s surprising role in early brain formation
An ‘atlas’ of the choroid plexus across the lifespan
Once viewed merely as a producer of the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) bathing the brain and spinal cord, the choroid plexus is now known to be a key player in brain development and immunity. These fronds of brain tissue, located in the CSF-filled brain cavities known as ventricles, secrete instructive cues into the CSF to regulate ... Read More about An ‘atlas’ of the choroid plexus across the lifespan
Motor neurons made from patients’ cells reveal possible ALS drugs and targets
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) is a severe, fatal neurodegenerative disorder causing loss of motor neurons and voluntary muscle action. While mouse studies have identified potential treatments, these drugs have typically done very poorly in human trials. “One of the most difficult challenges in drug discovery is identifying a target that has a key role in ... Read More about Motor neurons made from patients’ cells reveal possible ALS drugs and targets
What drives severe lung inflammation in COVID-19?
A main feature of COVID-19 is lung inflammation and respiratory failure caused by an overexuberant immune response known as the cytokine storm. But why does the body produce such an excess of cytokine immune cells? New research from Talal Chatila, MD, of the Division of Immunology at Boston Children’s Hospital and colleagues provides some insights, ... Read More about What drives severe lung inflammation in COVID-19?
Recommendations for reproducibility in stem cell research
The ability to program induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) and drive their differentiation into a variety of neural cells is essential for studying neurological disorders, including intellectual and developmental disabilities (IDDs). But issues regarding variability and reproducibility from lab to lab make translating discoveries difficult, in turn slowing the progress of IDD research. To address ... Read More about Recommendations for reproducibility in stem cell research
New technique yields potential treatment for a common cause of autism
Since 2008, we have known that the 16p11.2 chromosomal region is linked with autism spectrum disorder (ASD). Now, researchers from Boston Children’s have developed a new way to study the effects of 16p11.2 deletion in human neurons. In the process, they also found a potential treatment, possibly expanding the therapeutic options for this specific cause ... Read More about New technique yields potential treatment for a common cause of autism
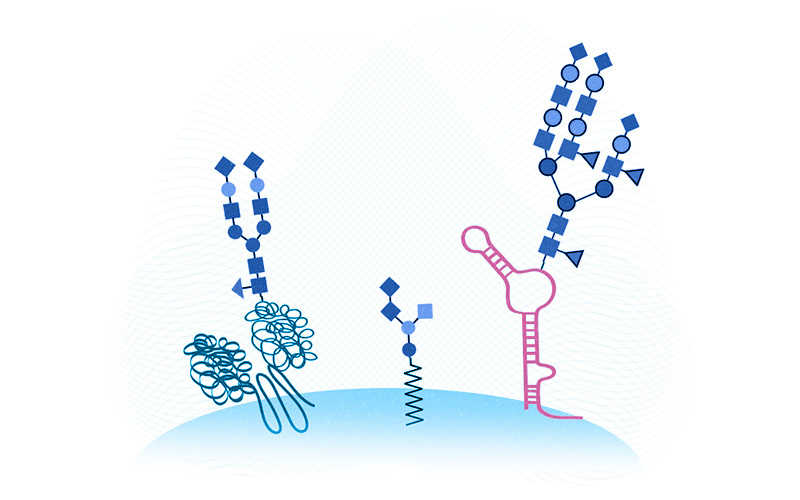
When worlds collide: Glycosylated RNAs upend cell biology as we know it
Cells in our body bristle with sugars known as glycans that other cells can recognize via specialized receptors. Glycans attach to and modify proteins and fats, thereby influencing how proteins fold, how cues are trafficked between cells, and other cell-to-cell interactions. As just one example of glycans’ importance, our blood types (A, B, O) depend ... Read More about When worlds collide: Glycosylated RNAs upend cell biology as we know it
Piecing together the preterm infant microbiome
The human microbiome — the collection of microbes living in the gut — is now recognized as an important contributor to health and disease. The environment, the host, and microbe-microbe interactions are all likely to shape the microbiome’s dynamics, but the unique roles of each are not well understood. Now, a Boston Children’s Hospital infectious ... Read More about Piecing together the preterm infant microbiome