Not just a physical thing: The psychology of sports injuries and recovery
“Nobody plays sports expecting to get injured, but unfortunately, injuries are part of sports,” says Melissa Christino, MD. As a surgeon in the Sports Medicine Division at Boston Children’s Hospital, Christino helps athletes recover from sports injuries, some of which keep her patients on the sidelines for weeks or months at a time. Key takeaways ... Read More about Not just a physical thing: The psychology of sports injuries and recovery
Trial for severe asthma targets a mutation common in children of color
Children and adults of color have higher rates of asthma than white people, as well as more hospitalizations and deaths. There are many reasons for this disparity, including more exposure to allergens and pollutants and differences in asthma care. One difference, however, is genetic. A mutation that causes severe, hard-to-treat asthma, in the gene ILR4, ... Read More about Trial for severe asthma targets a mutation common in children of color
Unpacking the body’s interferon response to COVID-19
Interferons are potent natural antivirals, rallying other parts of the immune system to defend against viruses. Some clinical trials have tested interferons as a treatment for COVID-19, but results have been mixed. And the science has been unclear about whether interferons are helpful or harmful. Key takeawayAn early, protective interferon response in the upper respiratory ... Read More about Unpacking the body’s interferon response to COVID-19
Why do some children get MIS-C after COVID-19? Some early clues
Several months into the COVID-19 pandemic, a small number of children began to develop a cluster of mysterious symptoms. These included rashes, red eyes, gastrointestinal symptoms and, most worrisome, heart problems. Why does this serious illness, now known as multisystem inflammatory disorder in children (MIS-C), strike some previously healthy children? And who is most at ... Read More about Why do some children get MIS-C after COVID-19? Some early clues
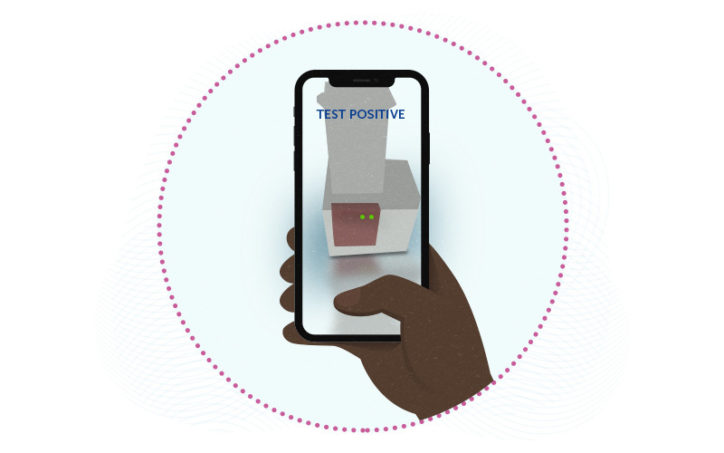
Rapid saliva test detects COVID-19 variants, at home or point of care
COVID-19 tests are now widely available, including FDA-approved tests like BinaxNOW that people can do at home. But none of the home tests — or any hospital test — can distinguish between specific SARS-CoV-2 variants. Detecting and tracking variants, essential for public health efforts, requires complete nucleic acid sequencing of the virus. Currently, only specialized ... Read More about Rapid saliva test detects COVID-19 variants, at home or point of care
RNA-modifying protein offers a possible lead for treating aggressive cancers
A protein that modifies RNAs, called METTL1, could be a target for treating some aggressive, difficult-to-treat cancers, suggests new research in Molecular Cell. The study provides evidence that blocking METTL1 curbs cancer cells’ ability to grow, selectively killing them, and the researchers believe it could be targeted with drugs. METTL1 and related proteins had previously ... Read More about RNA-modifying protein offers a possible lead for treating aggressive cancers
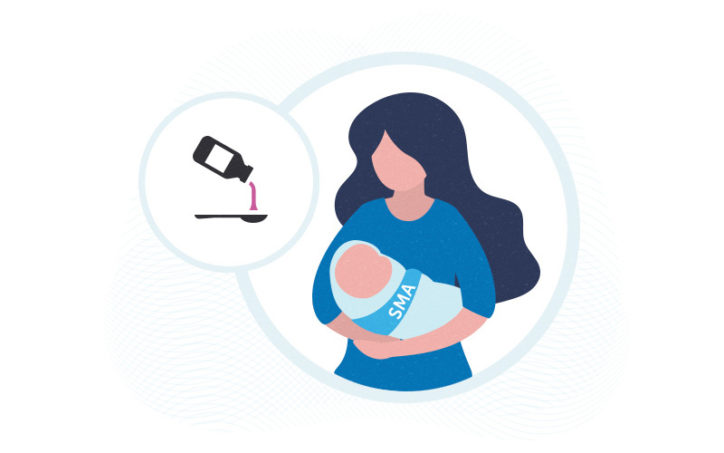
Risdiplam improves motor function in infants with spinal muscular atrophy
Until recently, babies and children with spinal muscular atrophy (SMA) lacked any type of treatment capable of stopping the neuromuscular disease from progressing. In SMA, damaged motor neurons in the spinal cord fail to correctly send messages to the muscle cells. As a result, infants and children with SMA may not be able to hold ... Read More about Risdiplam improves motor function in infants with spinal muscular atrophy
Thickened feeds — but not acid-suppressing medications — help treat laryngomalacia in infants
In laryngomalacia, the soft tissues of the larynx fall over the airway opening and partially block it, which can result in stridor, feeding difficulties, and other symptoms. Infants with this condition are frequently treated with acid-suppressing medications, based on the belief that gastroesophageal reflux might worsen the problem. However, there’s little evidence to support the ... Read More about Thickened feeds — but not acid-suppressing medications — help treat laryngomalacia in infants
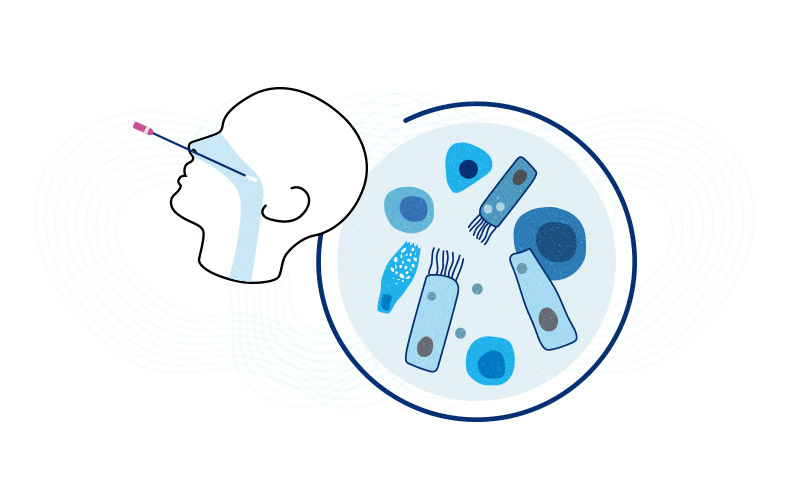
Why do some people get severe COVID-19? The nose may know
The body’s first encounter with SARS-CoV-2, the virus behind COVID-19, happens in the nose and throat, or nasopharynx. A new study in the journal Cell suggests that the first responses in this battleground help determine who will develop severe disease and who will get through with mild or no illness. Building on work published last ... Read More about Why do some people get severe COVID-19? The nose may know
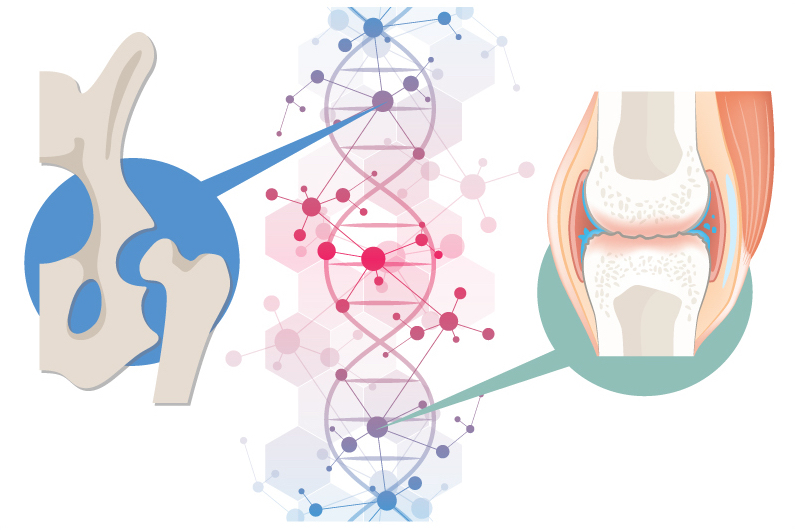
The surprisingly specific genetics of joint disease
A new study provides unexpected insights into the biology of two common, heritable orthopedic conditions: developmental dysplasia of the hip (DDH) and knee osteoarthritis (OA). The findings, published July 6 in Nature Communications, show how a gene can have different effects in different parts of the body. They also raise the possibility of preventive measures ... Read More about The surprisingly specific genetics of joint disease