Archive for cardiac research
First-of-its-kind pressurization test could improve Ross procedure outcomes
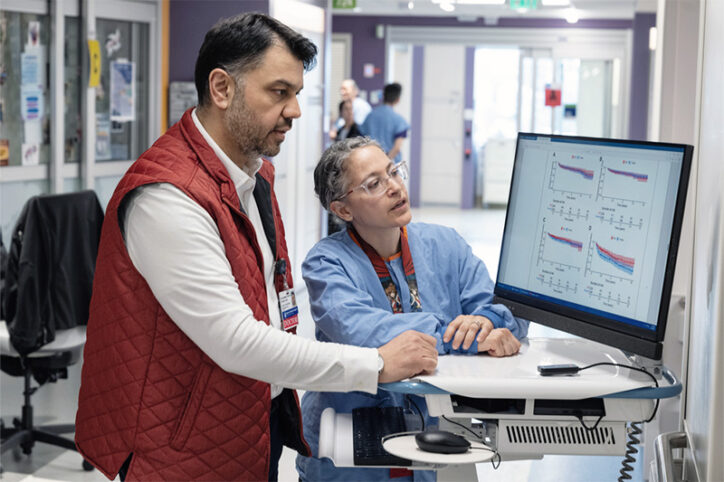
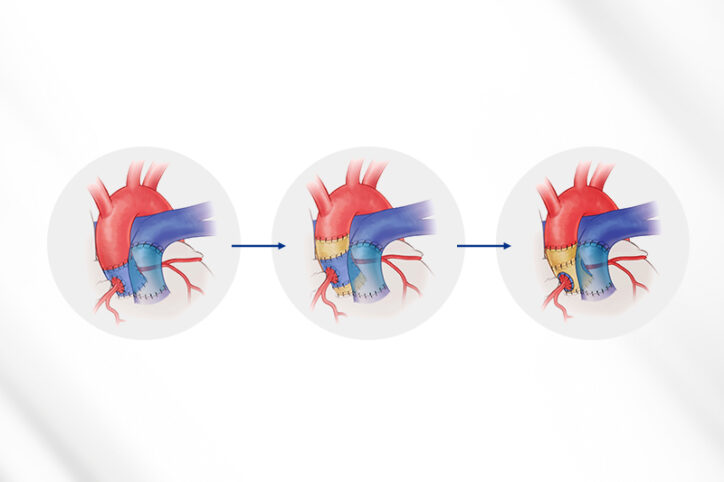
The Ross procedure is a preferred surgery to treat severe aortic valve disease. The procedure replaces the failing valve with a patient’s own pulmonary valve. It’s an effective treatment option, but some patients have had complications. After surgery, the root of their aortic valve — where the valve connects with the heart — enlarges and causes ... Read More about First-of-its-kind pressurization test could improve Ross procedure outcomes
Tagged: aortic valve, cardiac research, cardiac surgery, heart, heart center
Treating MAPCAs with unifocalization surgery and cardiology care
Children born with a rare form of tetralogy of Fallot (ToF) face a challenging type of congenital heart disease. Known as ToF with pulmonary atresia and major aortopulmonary collateral arteries (MAPCAs), the condition often requires a child to have many operations and cardiology procedures to restore blood flow to the lungs and protect their heart from damage. But a team ... Read More about Treating MAPCAs with unifocalization surgery and cardiology care
Advancing global health: Using AI to detect heart disease in children
In many low- and middle-income countries, pediatric cardiologists can’t help children with congenital heart conditions because of a critical hurdle. They don’t have easy access to advanced diagnostic technology. Key takeaways Children in many countries are not receiving proper heart care because they’re not being diagnosed. AI-powered electrocardiogram (AI-ECG) models could give cardiologists in these ... Read More about Advancing global health: Using AI to detect heart disease in children
Past patient outcomes could help single-ventricle surgery decisions
When considering whether a child who has a single-ventricle heart defect would benefit more from biventricular repair or the Fontan procedure, heart specialists have lacked a key tool to guide them: data that shows possible long-term health risks of each surgical option. But Boston Children’s heart specialists — who perform biventricular repair more often than any other pediatric hospital — ... Read More about Past patient outcomes could help single-ventricle surgery decisions
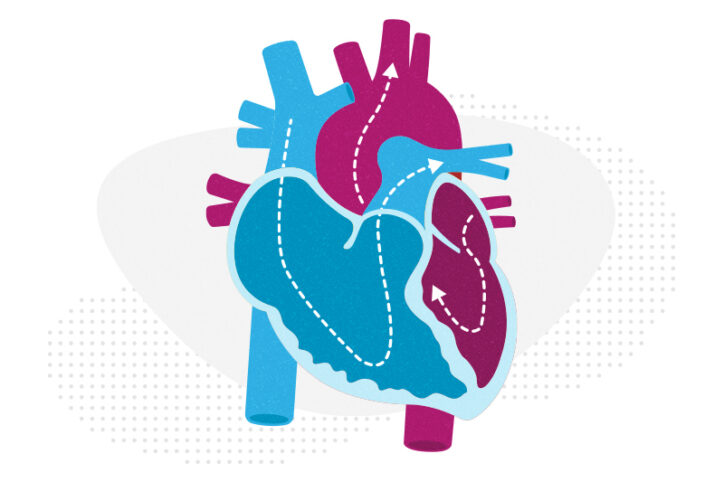
It’s all in the PV loops: New analytical model could improve circulation assessments before heart surgery
The double-switch operation corrects the congenital reversal of the heart’s ventricles and its two main arteries. It’s a practical way of putting the ventricles into the position they belong so that children with congenitally corrected transposition of the great arteries (CC-TGA) can benefit from enhanced circulation. Surgery, though, doesn’t come without risks. Some children’s left ventricles — ... Read More about It’s all in the PV loops: New analytical model could improve circulation assessments before heart surgery
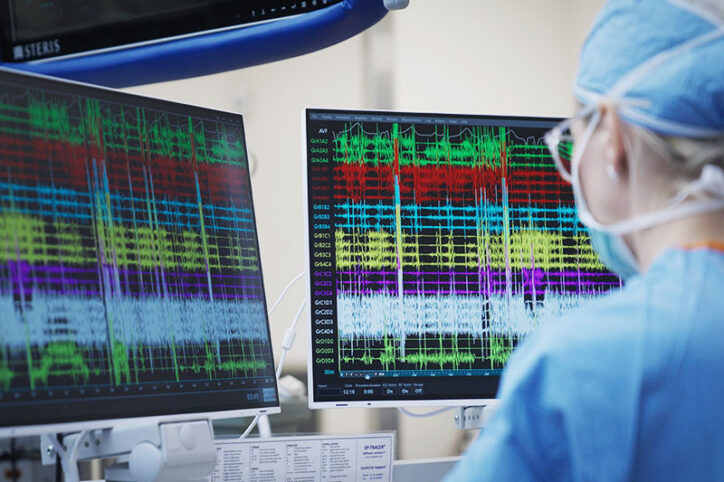
Conduction tissue mapping is shown to significantly reduce heart block
New research by Boston Children’s validates an innovative approach to mapping the heart’s invisible conduction tissue during surgery. Key takeaways Using a catheter to map unseen conduction tissue drastically reduces heart block during biventricular repair surgeries for several heart conditions. Conduction tissue was identified in 96 percent of patients who were mapped. Only 4 of ... Read More about Conduction tissue mapping is shown to significantly reduce heart block
Injected microbubbles could be a safe way to deliver emergency oxygen
For years, researchers and clinicians have been trying to find a way to rapidly deliver oxygen to patients when traditional means of oxygenation are difficult or ineffective during critical moments of cardiac or respiratory arrest. Sometimes, hypoxemia caused by airway obstruction or lung disease can be so severe that methods to boost low-oxygen levels (including ... Read More about Injected microbubbles could be a safe way to deliver emergency oxygen
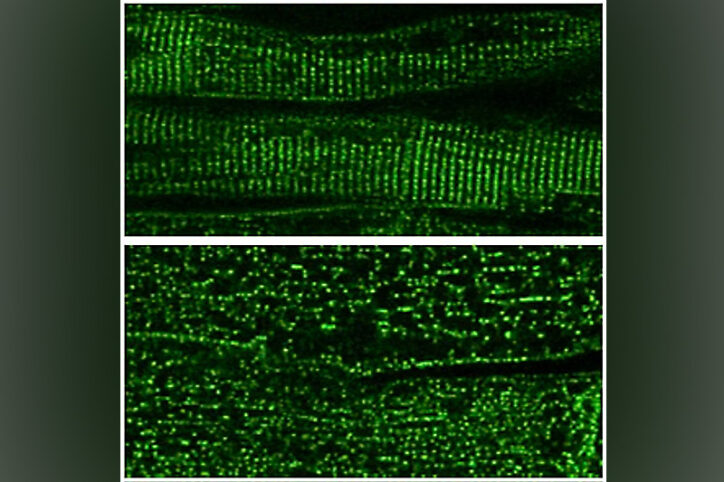
Shoring up heart muscle’s mini ‘managers’ to treat heart failure
Our heart muscle is studded with tiny dyads, intricately designed structures that manage incoming electrical signals and calcium release to coordinate our heartbeats. Could gene therapy help maintain dyads’ structure and boost the function of failing hearts? A new study suggests it can. “We know that in heart failure from many causes, dyads become disorganized,” says ... Read More about Shoring up heart muscle’s mini ‘managers’ to treat heart failure
Finding a possible genetic treatment for rare arrhythmias
Variants in a gene that plays a key role in heart function can cause potentially life-threatening arrhythmia syndromes known as calmodulinopathy. Calmodulinopathy is rare and causes arrhythmias that are poorly treated by current options. Boston Children’s cardiologist William Pu, MD, believes he has found a promising custom genetic treatment: antisense oligonucleotides that deplete the disease-causing gene product. ... Read More about Finding a possible genetic treatment for rare arrhythmias
Eight years of preparation for a surgical first: a partial heart transplant
Boston Children’s cardiac surgeons have an overriding goal for each patient: If possible, repair their congenital heart defect (CHD) — rather than replace any native heart tissue. Preserving heart tissue often leads to a speedier and more complete recovery and longer-lasting cardiac function. Sometimes, though, a patient’s valve tissue is beyond repair and a bioprosthetic or mechanical replacement valve ... Read More about Eight years of preparation for a surgical first: a partial heart transplant