Changing lives through genetics: The Children’s Rare Disease Collaborative
A 14-year-old girl was having back pain after a car accident and visited an orthopedic clinic at Boston Children’s Hospital. In the course of her care, she joined the Children’s Rare Disease Collaborative (CRDC), a hospital-wide effort to enroll children and adults with rare diseases in genetic studies. Genetic testing revealed that both she and ... Read More about Changing lives through genetics: The Children’s Rare Disease Collaborative
Model enables study of age-specific responses to COVID mRNA vaccines in a dish
mRNA vaccines clearly saved lives during the COVID-19 pandemic, but several studies suggest that older people had a somewhat reduced immune response to the vaccines when compared with younger adults. Why? Researchers at Boston Children’s Hospital, led by Byron Brook, PhD, David Dowling, PhD, and Ofer Levy, MD, PhD, found some answers — while providing ... Read More about Model enables study of age-specific responses to COVID mRNA vaccines in a dish
Could a pill treat sickle cell disease?
The new gene therapies for sickle cell disease — including the gene-editing treatment Casgevy, based on research at Boston Children’s Hospital — have been game-changing for the patients who have received them. But Stuart Orkin, MD, the Boston Children’s hematologist whose work led the way to Casgevy, wants to go even further. “The editing therapy ... Read More about Could a pill treat sickle cell disease?
A sickle cell first: Base editing, a new form of gene therapy, leaves Branden feeling ‘more than fine’
Though he doesn’t remember it, Branden Baptiste had his first sickle cell crisis at age 2. Through elementary school, he was in and out of the hospital with pain episodes, not knowing why. As he got older, he learned he had sickle cell disease. His red blood cells were forming sickle shapes and getting stuck ... Read More about A sickle cell first: Base editing, a new form of gene therapy, leaves Branden feeling ‘more than fine’
Injected microbubbles could be a safe way to deliver emergency oxygen
For years, researchers and clinicians have been trying to find a way to rapidly deliver oxygen to patients when traditional means of oxygenation are difficult or ineffective during critical moments of cardiac or respiratory arrest. Sometimes, hypoxemia caused by airway obstruction or lung disease can be so severe that methods to boost low-oxygen levels (including ... Read More about Injected microbubbles could be a safe way to deliver emergency oxygen
A universal gene therapy for Diamond-Blackfan anemia is poised for clinical testing
Diamond-Blackfan anemia (DBA), first described at Boston Children’s Hospital in 1938, is a rare blood disorder in which the bone marrow cannot make mature, functioning red blood cells. Children with this life-threatening anemia have few treatment options. A small handful with a well-matched donor can be cured with bone marrow transplant, but most rely on ... Read More about A universal gene therapy for Diamond-Blackfan anemia is poised for clinical testing
Skin organoid could guide new treatments for skin conditions, hair loss
What does it take to build healthy skin? Two research groups converged on this question from different angles. They’ve now produced the most detailed view to date of the cell types and cell collaborations that go into creating our body’s largest organ. Several years ago, Karl Koehler, PhD, and colleagues at Boston Children’s Hospital used ... Read More about Skin organoid could guide new treatments for skin conditions, hair loss
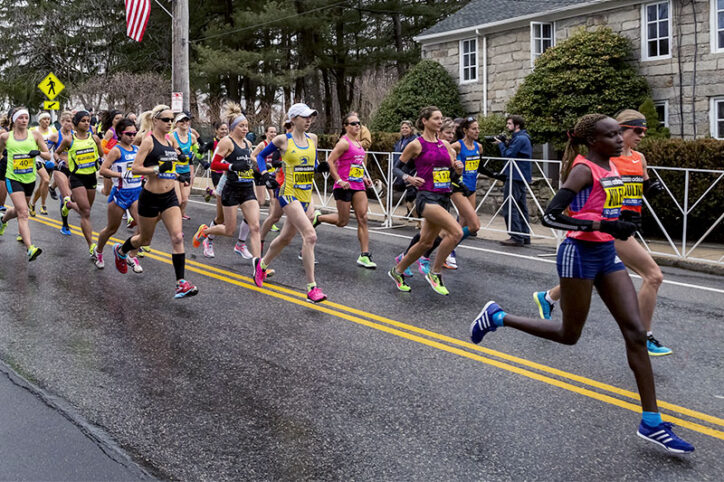
Fuel to be faster: Studying the effects of low energy availability at the Boston Marathon
Like many sports medicine specialists, Kristin Whitney, MD, MA, suspected that many of the issues she treats in runners — bone stress injuries, anemia, decreased response to training, and reduced endurance to name a few — stemmed from insufficient nutrition. Key takeaways Runners with indicators of low energy availability had slower finish times and more ... Read More about Fuel to be faster: Studying the effects of low energy availability at the Boston Marathon
Making pediatric health equity research truly equitable: An EDI review process
A burgeoning number of studies are examining pediatric health equity, diversity, and inclusion (EDI). But if not done right, health equity research can do a disservice, perpetuating biases and wrong assumptions that actually exacerbate inequities. To guide EDI-related studies, the Institutional Review Board (IRB) at Boston Children’s Hospital (through Tina Young Poussaint, MD, and Susan ... Read More about Making pediatric health equity research truly equitable: An EDI review process
Mutations during prenatal development may contribute to schizophrenia
Schizophrenia is known to have a genetic component, and variants in 10 genes have been identified as markedly increasing schizophrenia risk. But together, these genes account for under 5 percent of cases. Now, a pilot study in the journal Science suggests another important contributor to schizophrenia: distinctive patterns of non-inherited (somatic) mutations. These mutations appear ... Read More about Mutations during prenatal development may contribute to schizophrenia