Science seen: A “wheel of death” for bacteria
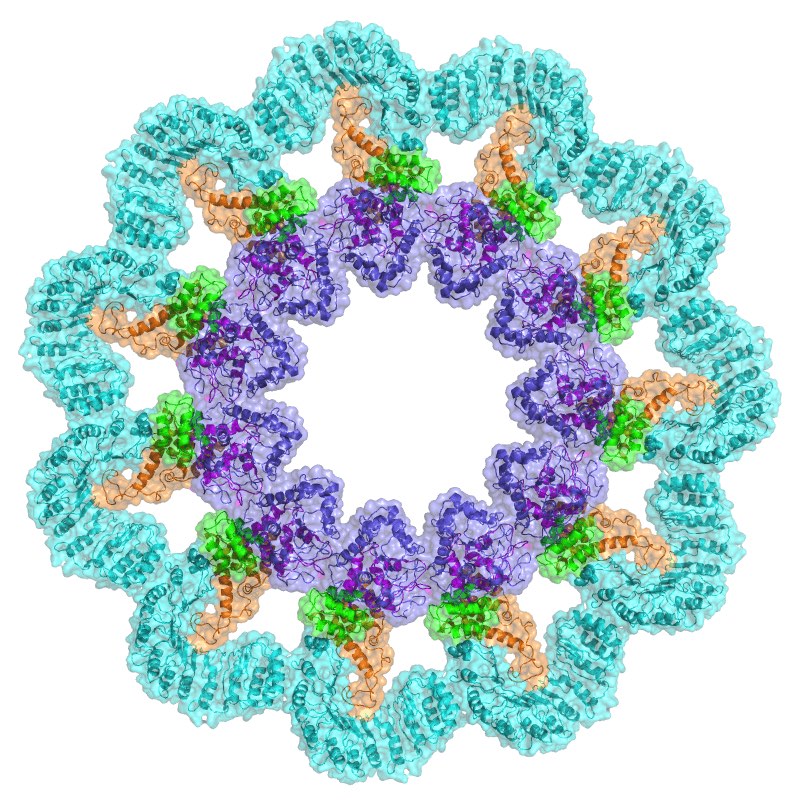
The innate immune system acts like a border patrol for the body, picking up bacteria and other invading pathogens using molecular sensors. One key player is the inflammasome, a multi-protein complex depicted here through cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM). Using structural biology tools like cryo-EM and X-ray crystallography, the Wu lab in Boston Children’s Hospital’s Program in Cellular and Molecular Medicine show how protein components come together in inflammasomes to form a “wheel of death” against bacterial infection.
Once they detect an invader, inflammasomes send out signals that trigger infected cells to die using an inflammatory death pathway called pyroptosis. They also call for backup from the adaptive immune system, in the form of inflammation. (Image: Wu laboratory/Liman Zhang)
Related Posts :
-

Building better antibodies, curbing autoimmunity: New insights on B cells
When we’re vaccinated or exposed to an infection, our B cells spring into action, churning out antibodies that are ...
-

Exposing a tumor’s antigens to enhance immunotherapy
Successful immunotherapy for cancer involves activating a person’s own T cells to attack the tumor. But some tumors have ...
-

Could we intervene in Huntington’s disease before symptoms appear?
Huntington’s disease is the most common single-gene neurodegenerative disorder and is characterized by motor and cognitive deficits and psychiatric ...
-

Could the right dietary fat help boost platelet counts?
Aside from transfusions, there currently is no way to boost people’s platelet counts, leaving them at risk for uncontrolled ...