The neurology resident that could
Elizabeth Engle used to wait in peoples’ driveways until midnight, hoping to enroll them in her genetic studies of eye-movement disorders. She landed there by chance: during her neurology residency, she saw a little boy whose eyes were frozen in a downward gaze. Wanting to find a solution to a disorder that others had written off, she talked her way into the muscular dystrophy genetics lab of Alan Beggs and Lou Kunkel at Children’s.
Why muscular dystrophy? That tragic muscle-weakening disease somehow spares the eye muscles. Engle thought if Beggs and Kunkel took her on, she could answer two questions at once – what was protecting the eye muscles in muscular dystrophy, and what had caused the little boy’s fixed gaze and droopy eyelids. Plus, she needed laboratory training to study the samples she’d started gathering. “I didn’t have a PhD and was never officially trained in the lab,” she once said. “I didn’t even know how to make chemical solutions.”
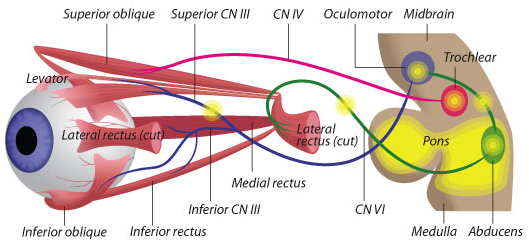
Engle’s research career was launched – bringing her into a world of inherited, socially isolating disorders that rob people of the ability to control their eye movements – leaving multiple family members with droopy lids, or unable to look left or right, or up and down, without tilting their head. Or sometimes a combination of these.
Breaking ground in genetic eye-movement disorders
Engle now has a database of more than 1,500 patients from all over the world (who now mostly mail their DNA samples) and multiple genetic discoveries to her credit. Though it seems she occupies a rather odd niche in ophthalmology, she’s also broken new ground in neuroscience – since, ultimately, it’s faulty nerve development and guidance that cause these disorders.
Having written about Engle’s science on several occasions, I’ve seen her tenacity firsthand. But I now appreciate her as a scientific adventurer, willing to step out of her comfort zone, learn new tricks and do whatever it takes to see a problem through. Read more in this wonderful profile in the HHMI Bulletin.
Related Posts :
-

The dopamine reset: Restoring what’s missing in AADC deficiency
In March 2023, a young girl came to Boston Children’s Hospital unable to hold up her head — one striking symptom ...
-

New research sheds light on the genetic roots of amblyopia
For decades, amblyopia has been considered a disorder primarily caused by abnormal visual experiences early in life. But new research ...
-

Parsing the promise of inosine for neurogenic bladder
Spinal cord damage — whether from traumatic injury or conditions such as spina bifida — can have a profound impact on bladder ...
-

Thanks to Carter and his family, people are talking about spastic paraplegia
Nine-year-old Carter may be the most devoted — and popular — sports fan in his Connecticut town. “He loves all sports,” ...